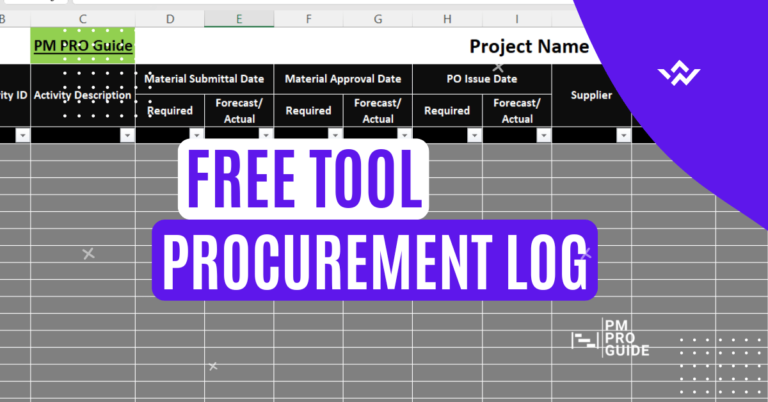
In the world of construction project management, delay analysis plays a pivotal role in identifying the causes of project delays and resolving disputes. Two widely used methods for delay analysis are “Retrospective Delay Analysis” and “Prospective Delay Analysis.” In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of these two approaches, highlighting their differences, benefits, and applications. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of each method, enabling you to make informed decisions and effectively manage construction project delays.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Delay Analysis
Delay analysis is a critical process in construction project management, as it helps stakeholders understand the reasons behind project delays and allocate responsibility appropriately. It involves the identification and assessment of delays, providing valuable insights into the impact on the overall project schedule and cost.
2. Retrospective Delay Analysis
Retrospective Delay Analysis, also known as “As-Built Delay Analysis,” is a method used to analyze project delays after they have occurred. This approach involves a meticulous examination of project records, documents, and communications to determine the timeline of events leading to the delay.
2.1 Methodology
In retrospective delay analysis, the following steps are typically followed:
- Identification of Critical Events: The first step is to identify the critical events that significantly impacted the project timeline. These events can include weather conditions, design changes, material shortages, labor issues, etc.
- As-Built Schedule Preparation: The project’s as-built schedule is prepared, detailing the actual sequence of activities and the time taken for each task.
- Baseline Schedule Comparison: A comparison is made between the baseline schedule (the original plan) and the as-built schedule to determine the variances.
- Causation Analysis: An in-depth analysis is conducted to ascertain the causes of delays and their effects on the project.
- Delay Apportionment: The responsibility for each delay event is apportioned among the relevant parties based on the analysis.
2.2 Advantages of Retrospective Delay Analysis
- Offers a detailed historical perspective on project delays.
- Provides insights for future project planning and risk mitigation.
- Allows stakeholders to learn from past mistakes and improve project management strategies.
3. Prospective Delay Analysis
Prospective Delay Analysis, also referred to as “As-Planned vs. As-Built Analysis,” is a forward-looking method used to assess the potential impact of delay events on a construction project. This approach is valuable when ongoing projects face potential delays, and proactive measures are necessary.
3.1 Methodology
The process of prospective delay analysis involves the following key steps:
- Identification of Potential Delay Events: Project teams identify and analyze potential delay events that may arise during the course of the project.
- As-Planned Schedule Preparation: The original project schedule, known as the “As-Planned” schedule, is created without considering any potential delays.
- As-Built Schedule Development: Simultaneously, the “As-Built” schedule is prepared, considering the actual progress and any delays that have occurred.
- Comparison and Analysis: The As-Planned and As-Built schedules are compared and analyzed to predict the impact of potential delay events.
- Mitigation Strategies: Based on the analysis, proactive measures are devised to mitigate the impact of potential delays.
3.2 Advantages of Prospective Delay Analysis
- Enables project teams to anticipate and prevent potential delays before they occur.
- Facilitates better decision-making by providing insights into possible risks and their effects on the project schedule.
- Helps in the development of effective contingency plans.
4. Choosing the Right Delay Analysis Method
The selection of the appropriate delay analysis method depends on various factors, such as the project’s stage, data availability, complexity, and contractual requirements. Both retrospective and prospective delay analysis have their merits, and the best choice will depend on the specific circumstances of the project.
To determine the most suitable approach, project stakeholders must carefully consider their goals and objectives, as well as the level of detail required to address the delay issues effectively.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, delay analysis is an indispensable tool in the construction project management toolkit. Retrospective Delay Analysis offers a valuable historical perspective, allowing stakeholders to learn from past experiences and improve future projects. On the other hand, Prospective Delay Analysis empowers project teams to be proactive in addressing potential delays and mitigating their impact.
By understanding the nuances of each approach, project managers can make informed decisions, minimize disputes, and ensure the successful and timely completion of construction projects.